With exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, high strength, and lightweight properties, titanium alloy has become an ideal material in the medical field, occupying a pivotal position in both Western and Chinese medical systems.
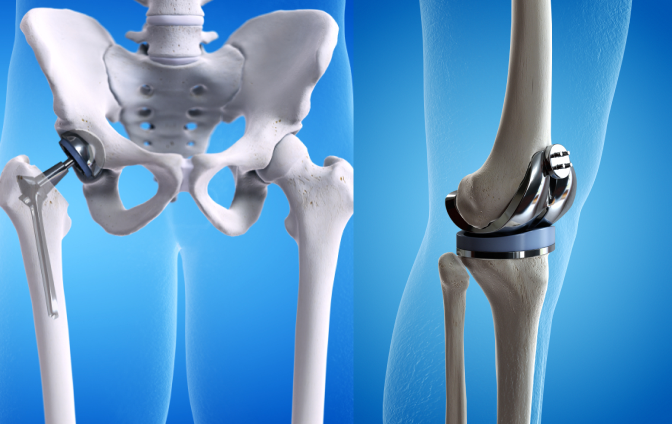
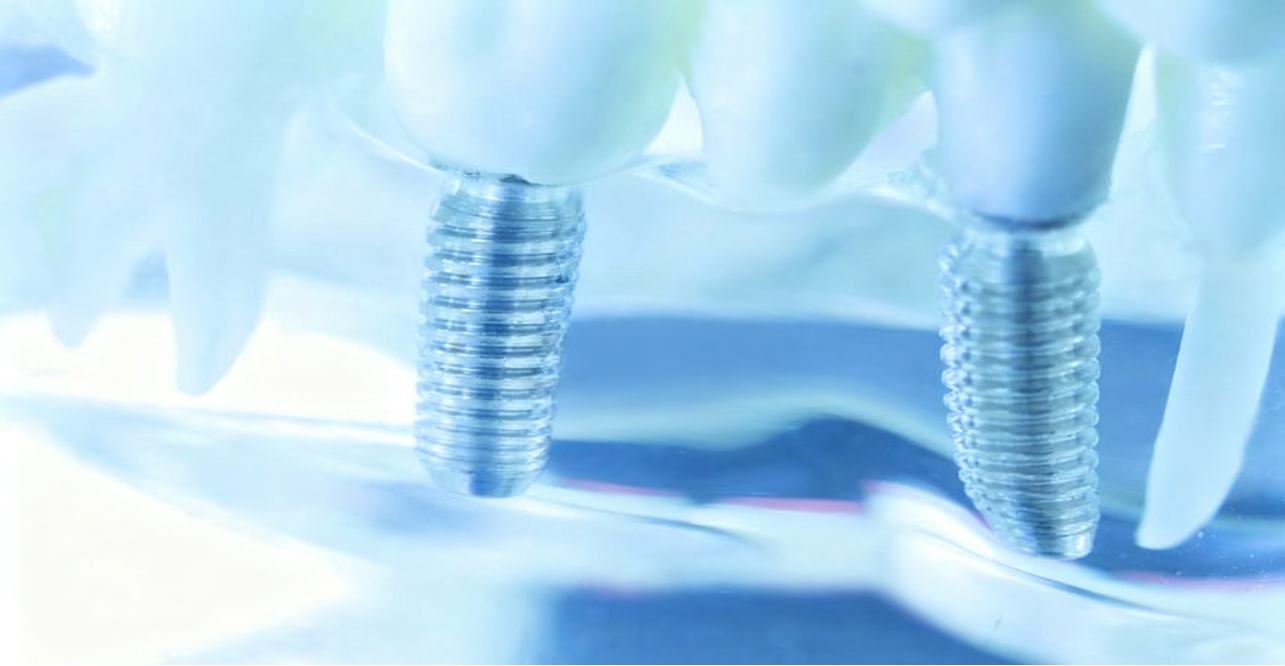
In implant medicine, titanium alloy is the top choice for orthopedics and dentistry. It is perfectly compatible with human tissues without causing rejection reactions, and is often used in artificial joints, trauma fixation plates, dental implants, and more. Its strength is close to that of human bones, while its weight is only 60% that of stainless steel, reducing the physical burden after implantation. It can also resist corrosion by body fluids, boasting a service life of decades.

In the field of surgical instruments, tools such as scalpels and hemostats made of titanium alloy are not only sharp and durable but also low in allergenicity, reducing the risk of patient infection, being widely adopted by top hospitals in Europe and the United States as well as local medical institutions in China. Additionally, in precision medical devices like cardiovascular stents and artificial heart valves, the processing flexibility and biosafety of titanium alloy are fully utilized.
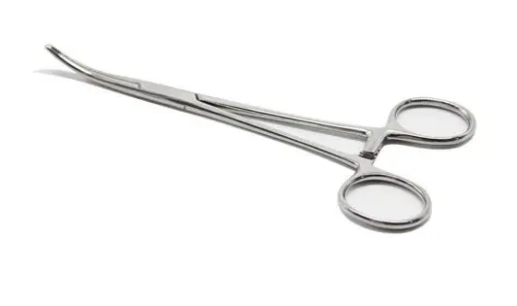
From high-end Western medical equipment to localized medical innovation in China, titanium alloy, with the advantage of "combining performance and safety," is driving the development of global medical technology towards a more precise and long-lasting direction.